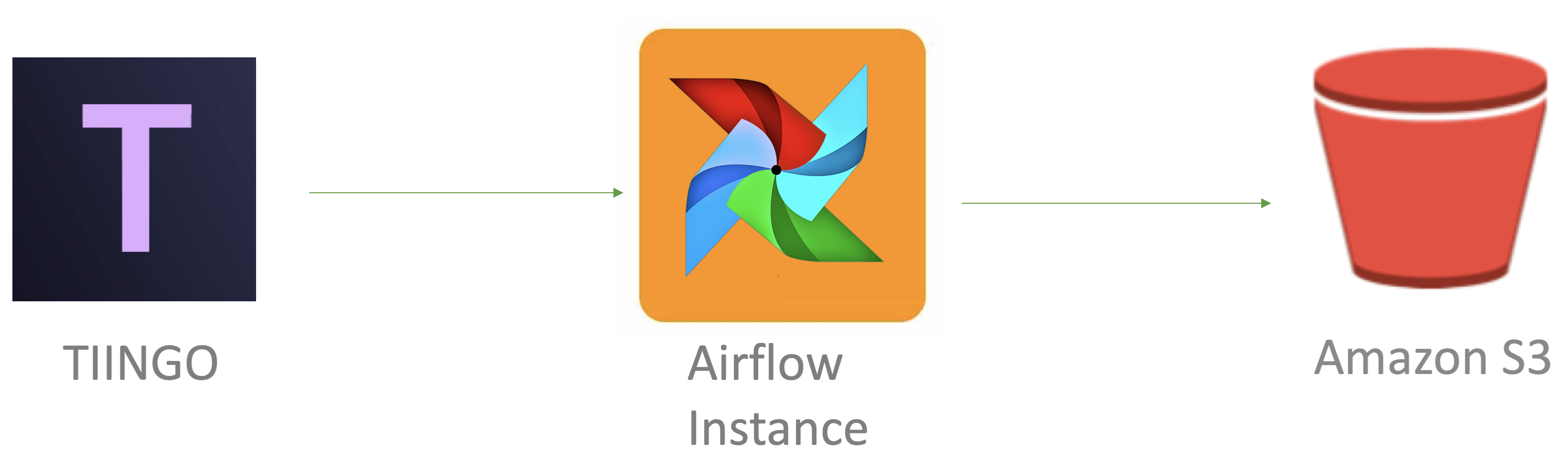
This tutorial is to set up airflow locally (or on an AWS instance, if you follow the steps in this article ). We’ll use airflow to create a DAG that gets stock data every weekday at 5 pm and stores the data in an AWS S3 bucket. Below is the workflow for this process.
Assumptions
- You already have aws-cli installed with your aws credentials stored locally (or in aws instance)
- You already have a TIINGO account with an associated API key
Terms
- DAG - Dynamic Acyclic Graph. The main workflow component of airflow. It’s an acyclic graph where jobs are executed in a sequence.
- Operator - Defines a task that needs to be performed. Examples include PythonOperator (runs python command), BashOperator (runs bash command), and MySQLOperator (runs SQL commands).
- Task - what needs to be executed.
1. Installation
Installing airflow can be found here. For now, we’ll stick with the basic configurations (SequentialExecutor). There are ways to change this to use LocalExecutor or CeleryExecutor (to make the operators execute in parallel), but that’ll involve changing the default sql configurations.
2. Create DAG
from airflow.models import DAG
from airflow.operators.python_operator import PythonOperator
from airflow.operators.dummy_operator import DummyOperator
from datetime import date, timedelta, datetime
import pandas_datareader as pdr
from pandas_datareader.tiingo import TiingoDailyReader
from io import StringIO
import boto3
# Task to extract data from TIINGO
def get_stock_data(**kwargs):
start = datetime(2015, 1, 1)
end = datetime.now()
api_token="INSERT TIINGO API TOKEN HERE"
df = TiingoDailyReader(kwargs["params"]["stock"], start=start, end=end, api_key=api_token)
stock_df = df.read()
stock_df = stock_df.reset_index()
return stock_df
# Task to upload TIINGO data to AWS S3
def upload_to_s3(**kwargs):
# Communication with operators to upload data of current stock passed in kwargs parameters
ti=kwargs['ti']
df = ti.xcom_pull(task_ids=kwargs["params"]["stock_ti"])
stock = df['symbol'][0]
filename = stock + '_stock_df.csv'
# Upload to AWS S3
csv_buffer = StringIO()
df.to_csv(csv_buffer, index=False)
s3_resource = boto3.resource('s3')
s3_resource.Object('tech-stock-data', filename).put(Body=csv_buffer.getvalue())
# Default arguments to pass into DAG
default_args = {
'owner': 'hd2zm',
'depends_on_past': False,
'start_date': datetime(2019, 9, 12),
'retries': 1,
'retry_delay': timedelta(minutes=1)
}
# Schedule Interval written in CRON format to make sure it runs every weekday at 5 pm.
with DAG('stock_data', default_args=default_args, schedule_interval="0 17 * * 1-5") as dag:
start_task = DummyOperator(task_id='start')
# Extract data
get_amzn_stock_data = \
PythonOperator(task_id='get_amzn_stock_data',
provide_context=True,
python_callable=get_stock_data,
params={"stock": "AMZN"},
dag=dag)
get_msft_stock_data = \
PythonOperator(task_id='get_msft_stock_data',
provide_context=True,
python_callable=get_stock_data,
params={"stock": "MSFT"},
dag=dag)
get_fb_stock_data = \
PythonOperator(task_id='get_fb_stock_data',
provide_context=True,
python_callable=get_stock_data,
params={"stock": "FB"},
dag=dag)
get_aapl_stock_data = \
PythonOperator(task_id='get_aapl_stock_data',
provide_context=True,
python_callable=get_stock_data,
params={"stock": "AAPL"},
dag=dag)
get_googl_stock_data = \
PythonOperator(task_id='get_googl_stock_data',
provide_context=True,
python_callable=get_stock_data,
params={"stock": "GOOGL"},
dag=dag)
# Load data to S3
upload_amzn_to_s3 = \
PythonOperator(task_id='upload_amzn_to_s3',
provide_context=True,
python_callable=upload_to_s3,
params={"stock_ti": "get_amzn_stock_data"},
dag=dag)
upload_msft_to_s3 = \
PythonOperator(task_id='upload_msft_to_s3',
provide_context=True,
python_callable=upload_to_s3,
params={"stock_ti": "get_msft_stock_data"},
dag=dag)
upload_fb_to_s3 = \
PythonOperator(task_id='upload_fb_to_s3',
provide_context=True,
python_callable=upload_to_s3,
params={"stock_ti": "get_fb_stock_data"},
dag=dag)
upload_aapl_to_s3 = \
PythonOperator(task_id='upload_aapl_to_s3',
provide_context=True,
python_callable=upload_to_s3,
params={"stock_ti": "get_aapl_stock_data"},
dag=dag)
upload_googl_to_s3 = \
PythonOperator(task_id='upload_googl_to_s3',
provide_context=True,
python_callable=upload_to_s3,
params={"stock_ti": "get_googl_stock_data"},
dag=dag)
end_task = DummyOperator(task_id='end')
# Set dependencies
start_task.set_downstream([get_amzn_stock_data, get_msft_stock_data,
get_fb_stock_data, get_aapl_stock_data,
get_googl_stock_data])
get_amzn_stock_data.set_downstream(upload_amzn_to_s3)
get_msft_stock_data.set_downstream(upload_msft_to_s3)
get_fb_stock_data.set_downstream(upload_fb_to_s3)
get_aapl_stock_data.set_downstream(upload_aapl_to_s3)
get_googl_stock_data.set_downstream(upload_googl_to_s3)
end_task.set_upstream([upload_amzn_to_s3, upload_msft_to_s3,
upload_fb_to_s3, upload_aapl_to_s3,
upload_googl_to_s3])
3. Run Airflow
airflow scheduler -D
airflow webserver -DYou want to include -D to run these two as daemon (in the background)
4. See Results.
Your S3 bucket should have the following files: FB_stock_df.csv, AMZN_stock_df.csv, AAPL_stock_df.csv, MSFT_stock_df.csv, GOOGL_stock_df.csv.
5. Kill process (optional)
If you want to stop airflow scheduler and webserver running in the background, then run the following commands.kill $(ps -ef | grep "airflow scheduler" | awk '{print $2}')
kill $(ps -ef | grep "airflow webserver" | awk '{print $2}')
